- in Personality by Tony
- |
- 2 comments
Big five personality traits: Who are you?
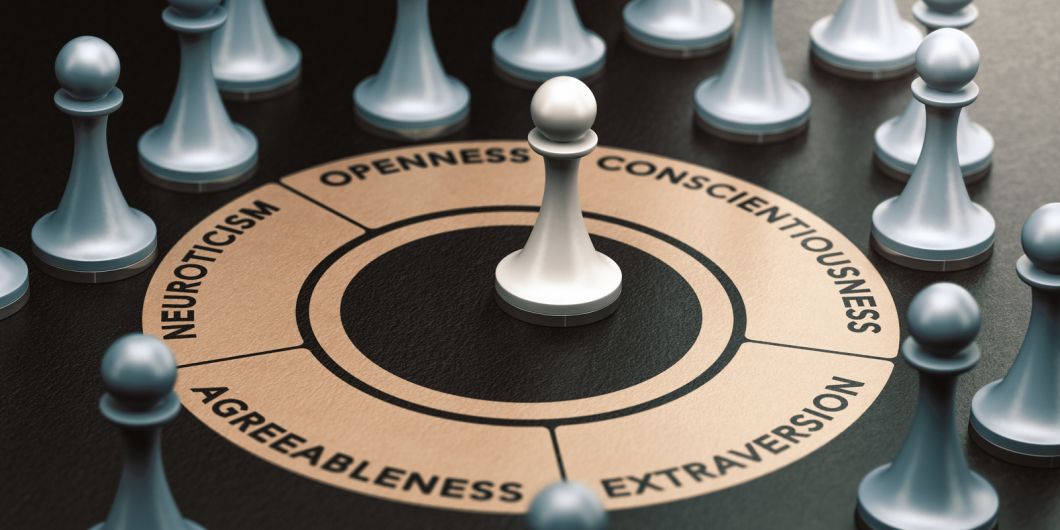

An individual’s personality traits define how they perceive the world around them. It is a set of characteristics and features that cause them to think, feel, and behave in a particular way.
Personality traits are characteristic of enduring behavioural and emotional patterns rather than isolated occurrences.
Although all aspects of your personality stem from both nature and nurture, many models of personality types attempt to explain why we are the way we are.
More...
People have probably been fascinated by personality traits since the first Homo sapiens roamed the earth. The first profound personality test was created in 1915, during the First World War.
Robert Woodworth’s “Psychoneurotic Inventory” was the forerunner of personality tests such as the Myers-Briggs test.
Such personality qualities seem more consistent over time, being heavily loaded genetically. Five of the most studied factors that genetically influence someone’s personality: Extraversion, Agreeableness, Openness, Conscientiousness, and Neuroticism.
Big 5 personality traits
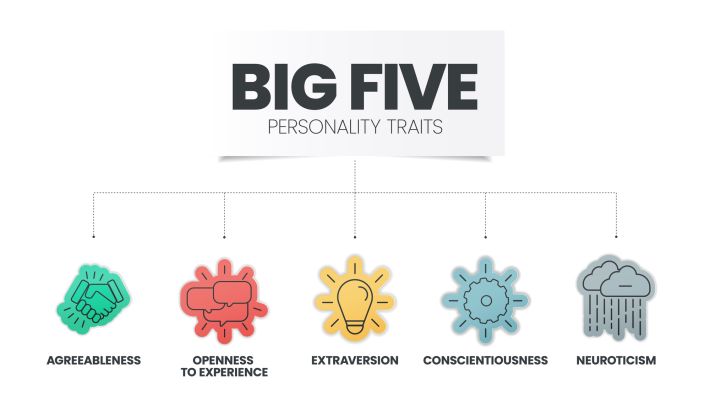
Whereas, personality traits are the most common way we tend to describe human behaviour in people. According to Goldberg's five factors of personality, OCEAN model. We all have a combination of the five traits.
(Openness, Conscientiousness, Extraversion, Agreeableness, Neuroticism) or you could use the mnemonic CANOE instead, depending on your nautical preference.
It is important to note that each of the five primary personality traits suggested could represent a range between two polar extremes with the Jungian dichotomy.
For instance, extraversion represents a continuum between extreme extraversion and extreme introversion. In the real world, most people lie somewhere in between.

The five factors are not necessarily traits in and of themselves, but factors in which many related traits and characteristics fit.
For example, the factor agreeableness encompasses terms like generosity, amiability, and warmth on the positive side and aggressiveness and temper on the negative side. All of these traits and characteristics (and many more) make up the broader factor of agreeableness.
Below, we’ll explain each factor in more details within each tab and provide examples and related terms to help you get a sense of what aspects and quirks of personality these factors cover.
Reference adapted from https://positivepsychology.com/big-five-personality-theory/
-
Openness to Experience
-
Extroversion
-
Agreeableness
-
Neuroticism
Openness to Experience
Openness to experience has been described as the depth and complexity of an individual’s mental life and experiences (John & Srivastava, 1999). It is also sometimes called intellect or imagination.
Openness-to-Experience’s facets include ‘fantasy; aesthetics; feelings; actions; ideas; values.’ People high in Openness-to-Experience tend to be open-minded and intellectual. They are more flexible with respect to rules and societal norms.
Openness to experience concerns people’s willingness to try to new things, their ability to be vulnerable, and their capability to think outside the box.
Those high in Openness have greater creative achievement in the arts.
Common traits related to openness to experience include:
- Imagination
- Insightfulness
- Varied interests
- Originality
- Daringness
- Preference for variety
- Cleverness
- Creativity
- Curiosity
- Perceptiveness
- Intellect
- Complexity/depth
An individual who is high in openness to experience is likely someone who has a love of learning, enjoys the arts, engages in a creative career or hobby, and likes meeting new people (Lebowitz, 2016a).
An individual who is low in openness to experience probably prefers routine to variety, sticks to what he or she knows, and prefers less abstract arts and entertainment.
It is when personality traits enter the extreme end of the continuum that they become problematic. For example, Cuban revolutionary, Fidel Castro, was said to be high in trait Openness-to-Experience, and led a Communist revolution. Conversely, very low Openness-to-Experience is strongly associated with an authoritarian personality.
Extraversion trait
For example, those with the extraversion trait are described as outgoing, talkative, and gregarious. Conversely, introversion is a preference for solitary or limited social situations. It’s worth noting, though, that most people are ambiverts - enjoying their own company occasionally and social experiences at other times.
Conscientiousness trait
This is a tendency to be reliable, self-disciplined, and organized. Somebody high in conscientiousness may be a perfectionist, stubborn, and obsessed with neatness to an extreme degree, while those at the other end may be careless, undisciplined, and impulsive.
Openness to experience trait
This trait describes a general approach to living that includes active curiosity, keen imagination, and a tendency to explore. At the other end of the scale, people tend to be factual, prosaic, and unimaginative.
Agreeableness trait
This trait is an overall tendency to be friendly and cooperative with other people instead of being suspicious and antagonistic. There is some evidence that it may increase with age.
Neuroticism trait

People high in neuroticism are likely to respond intensely emotionally to things around them. Those at the other end of the scale tend to be phlegmatic, calm, and unruffled. Neuroticism is one of the fundamental domains of general personality included within the Big Five.
Those high in neuroticism experience more anxiety and stress than those low on the spectrum. Neuroticism is often a precursor to other mental health issues, such as depression and addiction. They are also impacting a wide array of psychopathological, including personality disorders. They may be less likely to enjoy life and find satisfaction in activities.
Many people do not recognize their own neurotic personality or behaviours. Furthermore, each person might have a particular neurosis, but some people behave more neurotically than others. Being neurotic is best defined by behaviour. A few tendencies can be harmless when mild, but others can be dangerous.
Post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) could be considered a type of neurotic behaviour. You may have had terrifying experiences in a war, and if the sound of fireworks going off triggers a relapse, then you have experienced a neurotic episode. Similarly, you may have been abused by a parent when you were a child, and if you feel scared when you are alone around another adult, then you might be experiencing neuroticism.
Studies show that maturation may have an impact on the five personality traits. As people age, they become less extraverted, less neurotic, and less open to an experience. Agreeableness and conscientiousness, on the other hand, tend to increase as people grow older.
The Five Factor Model of Personality Traits aka The Big Five Video...
People can, of course, learn to adapt and behave in a way focused more on what is appropriate in a particular situation rather than what they would be led to do by their natural tendencies.
For instance, someone who tends to be more introverted than extroverted but takes a job as a teacher or salesperson will adapt to behave in a more extroverted way for work. With adaptability, they can surely do this. Yet, they may find their work roles more tiring than a naturally extroverted person.
Personality Disorder
Personality disorders are generally thought to arise from a combination of genetic factors and traumatic early life experiences such as parental loss and emotional, physical, and sexual abuse.
Features of Extreme Personality Traits Five Factor In Mental Health
Brain injury
Behavioural changes after brain injury are many and varied. Some appear to be an exaggeration of previous personality characteristics, while others may seem completely out of character for that person.
Disinhibition
A common change early in recovery is disinhibition, that is, loss of control over behaviour, resulting in socially inappropriate behaviour. This ranges from a tendency to divulge personal information too freely, to disturbing and unpredictable outbursts of uncontrolled rage.
Common complaints include a tendency to make tactless remarks, to laugh inappropriately, and to be over-familiar towards others.
Caregivers, therapists and nursing staff, need to be on their guard.
What is the difference between Introversion and Extroversion
In Conclusion

The Big Five personality traits are among the past’s most widely researched psychological concepts. They are among the most studied topics in psychology today because they explain why people behave the way they do.
Understanding what motivates us helps us better understand ourselves and our relationships with others. Evidence suggests that understanding how to manage your Big Five personality traits can help you become happier, healthier, and more successful.
In our opinion, the Big Five personality traits are the best model for describing human behaviour. This is because they describe the basic building blocks of human nature. Each trait represents a specific aspect of human character. For example, conscientiousness describes the degree to which someone is reliable, responsible, organized, and disciplined.
Openness describes the extent to which someone is creative, curious, imaginative, and open to change. Extroversion describes the tendency to seek out social interaction and stimulation. Agreeableness describes the degree to which we are cooperative, trusting, forgiving, helpful, friendly, and patient.
Neuroticism describes the tendency toward anxiety, depression, anger, hostility, jealousy, envy, guilt, insecurity, shame, embarrassment, fearfulness, vulnerability, and self-consciousness.
What's a long list if you happen to be on that scale, it may not give you all the answers now. Life experiences, pleasant or traumatic, can influence this scale.



[…] and egoistic are two terms used to describe different personality traits. Echoism refers to a personality type in which an individual tends to be excessively selfless, […]
[…] stated, procrastination is a trait that exists within all of us to some extent. It is correlated to conscientiousness, our sense of orderliness and dutifulness. People who are low in conscientiousness are more likely […]